Elements Lipids Are Made Of

Lipids are macromolecules, large organic molecules, that carry out many different functions needed for life. Lipids function to store energy, compose the membrane of cells, and act as chemical signalers. In terms of the elements plant in lipids, all lipids comprise oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon. Some lipids besides contain phosphorus and nitrogen. The elements that a lipid is fabricated out of depends upon the type of lipid and the part it carries out. Let's examine some of the dissimilar types of lipids. The four main types of lipids are sterols, phospholipids, waxes, and fats.
Backdrop Of Lipids
Lipids are somewhat different from other biological molecules because they are hydrophobic. Dissimilar hydrophilic (water-loving) molecules that dissolve in water, lipids don't dissolve when in the presence of water. You may take seen this property in action if you lot have looked at salad dressing. You'll notice that there is a vinegar layer, which is mostly water, and an oil layer. The h2o and oil form divide layers due to the hydrophobic properties of the lipids in the salad dressing.
Lipids are made out of a class of alcohol known as glycerol, fatty acids, and carbon. Carbon is the basic building block for all known organic molecules. Carbon atoms are found in all living things, and carbon is able to create such a various corporeality of life because it can form many unlike types of molecules. Lipids, like other organic molecules, are fabricated out a skeleton or base of operations created from carbon atoms and other molecules that attach themselves to the skeleton. When fatty acids and glycerol bond with the carbon-based skeleton, lipids are created. Lipids are broken downwardly past a process known as hydrolysis, and sure enzymes like lipase (a subclass of esterases) are responsible for starting this procedure.
Role Of Lipids
Lipids perform many different functions in the body. Lipids are compounds capable of storing chemicals and triglycerides function as energy storage/reserves of energy for the body. Lipids are also important compounds that comprise the prison cell membranes of cells in eukaryotic organisms. Lipids don't but role as components of the cell membrane, they as well regulate how permeable the membrane is. Lipids are even stores of fat soluble vitamins like vitamin A, D, East, and Grand.
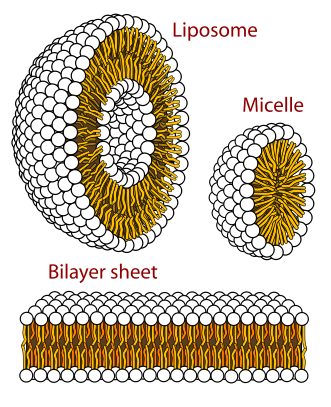
Lipids make upwards the phospholipid bilayer in prison cell membranes. Photograph: LadyofHats via Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain
Some lipids, such as steroid hormones and prostaglandins, function as metabolic regulators in the cell. Cholesterol itself is establish within the blood and cell membranes of most organisms. Cholesterol is what helps cell membranes maintain their fluidity, through the interaction between cholesterol and lipid complexes. Cholesterol is necessary for the creation of steroids, vitamin D, and bile acids. Polyunsaturated phospholipids give the membrane of cells flexibility and fluidity.
Lipoproteins are equanimous of proteins and lipids, and they are what permit lipids exist transported through aqueous environments and effectually the remainder of the body. Another class of lipids, fat acids (such as linolenic acids and linoleic acids) are necessary for the creation of a type of molecule called ecosanoids. Ecosanoids like thromboxanes and prostaglandins are involved in torso defense/repair and allowed system processes like blood clotting, inflammation, fever and pain.
Lipids role as electrical insulators for nervus fibers, with the lipids found in the myelin sheaths of the fibers. Lipids too part as signaling molecules, transmitting signals from cell to jail cell and system to system.
The Role Of Lipids In The Metabolism
Lipids play a critical role in the function of the metabolism, with sterols, phospholipids and triglycerides existence the primary types of lipids involved in the metabolic system. The lipid metabolism degrades sure lipids and synthesizes others, creating the functional lipids used in individual tissues.
Excess carbohydrates are broken down and converted into triglycerides, and this is accomplished through the utilization of acetyl-CoA and fatty acids. Acetyl-CoA is broken down and used to create fat acids, and the fatty acids then undergo a process known every bit esterification which creates triglycerides.
The fatty acids themselves are created through a synthesis process that reduces acetyl-CoA molecules. Unsaturated fatty acids can be synthesized through a process known as desaturation. During desaturation, double bonds are plugged into the fat acid chain. Linoleic acid is an instance of a double unsaturated fatty acid, and mammalian cells cannot synthesize it, meaning that mammals must eat organisms which accept created the acid to obtain it for themselves.
Acetyl-CoA is generated through the breakup of fatty acids by either peroxisomes or mitochondria. This breakup is referred to equally beta-oxidation. Two carbon fragments are broken off of the carboxyl end of the fatty acid, and the carbon fragments are used to generate acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA volition eventually be used to brand ATP through the electron transport concatenation of the citric acid cycle.
Types Of Lipids
Fats And Oils

Photo: margenauer via Pixabay, CC0
Saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and oils are structures are referred to as triglycerides, and they are created by the reaction of glycerol with one of several different fatty acids. These fats can either be liquid or solid at room temperature, depending upon how the triglyceride is structured.
Though you may have heard that saturated fats are healthier for y'all than unsaturated fats, the reason for this deviation isn't apparent until you know how the fats are dissimilar in their chemical makeup. The atoms of carbon institute in a molecule of glycolipids can only bond a maximum of iv times with other atoms. However, saturated fats operate a bit differently. Saturated fats have carbon atoms that form a single bond with atoms similar hydrogen in the molecule. This means that they create a long straight chain or tail of fatty acid that immune many molecules to be packed into a small corporeality of infinite. The effect of these long, tightly packed chains of saturated fats is that products which incorporate many saturated fats like butter or lard are often solid at room temperature. In contrast, unsaturated fats have carbon atoms that course double bonds with other atoms in the molecule. The double bonds end upward bending the tail of the fatty acid, and as a result of the molecules in the fatty acid tin't pack as tightly together as they can in saturated fats. Considering of this, products similar olive oil which take high unsaturated fatty content are usually liquid at room temperature.
Waxes
Waxes are organic compounds, much like fats. Waxes are usually comprised of long chains of hydrocarbons. Many of the natural waxes have something called esters within them. Esters are chemical compounds made out of at least ane alkoxy (O-alkyl) group, and they are unremarkably made out of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. Waxes frequently have long chain alcohols and long concatenation carboxylic acids.
Much similar fats and oils, waxes are usually insoluble in water. If you've always gone to a sandwich store and received a sandwich wrapped in wax paper, perhaps you've spilled water or something on the paper and seen how the wax repels the water away from it, how information technology forms beads on the surface of the wax paper and rolls off of it. Wax doesn't dissolve in water, and so this means that information technology's a useful compound for the creation of protective layers, something that many plants and other organisms have advantage of.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are a subtype of lipids that take a phosphate group within them. Phospholipids are major elements in the construction of cell membranes. Most phospholipids take a simple organic molecule like choline, a phosphate group, and a diglyceride. Because of this, phospholipids comprise nitrogen and phosphorous.
Phospholipids have a hydrophobic, or water-fugitive tail, and a hydrophilic or h2o-loving head. This forms what is known as the phospholipid bilayer. This phospholipid bilayer is what makes up the jail cell membrane and protects the organelles and other materials inside our cells from the outside world.
Steroids
Though it might be surprising to find out that steroids are lipids, if you know something about their properties information technology will come as less of a surprise. Much like other lipids, steroids are insoluble in water. Steroids include hormones similar estrogen and testosterone as well as cholesterol. Hormones are chemicals which transmit signals through the trunk and act to regulate the development and functions of the body. Steroids are made out of molecules of cholesterol and they are formed from carbon/hydrogen rings. Cholesterol is of import to maintaining the function of cell membranes, as it plays a role in the permeability and structure of the membranes.
Elements Lipids Are Made Of,
Source: https://sciencetrends.com/what-elements-are-in-lipids/
Posted by: samonsatrom1955.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Elements Lipids Are Made Of"
Post a Comment